Securing your cryptocurrency investments is paramount, and understanding the fundamentals of crypto wallets is the first step. This article, “The Basics of Crypto Wallets: How to Store Your Coins Safely,” will guide you through the essential aspects of crypto wallet management, covering different wallet types, including hardware wallets, software wallets, and online wallets. We’ll explore the security features of each, helping you choose the best option to safeguard your digital assets and navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency storage effectively. Learn how to protect your Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies from theft and loss with our comprehensive guide.
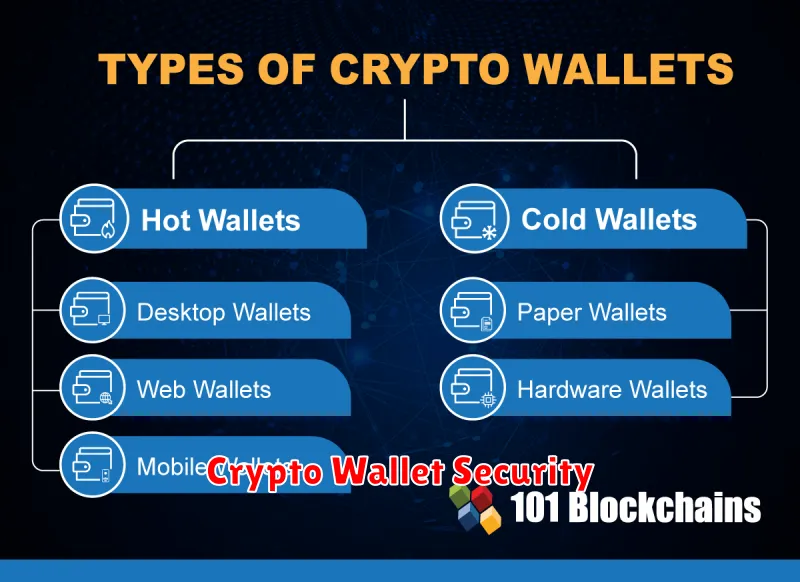
What is a Crypto Wallet?

A crypto wallet is a software or hardware device that allows you to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. It doesn’t actually hold the cryptocurrencies themselves; instead, it securely stores the private keys necessary to access and manage your digital assets on the blockchain.
Think of it like a digital bank account, but instead of holding fiat currency, it holds cryptocurrencies. Private keys are crucial; they are essentially passwords that prove your ownership of the cryptocurrency. Losing your private keys means losing access to your funds.
There are various types of crypto wallets, including hardware wallets (physical devices offering high security), software wallets (desktop, mobile, or web-based applications), and paper wallets (printed private keys for offline storage). The best type of wallet depends on your individual security needs and technical expertise.
Hot Wallets vs Cold Wallets
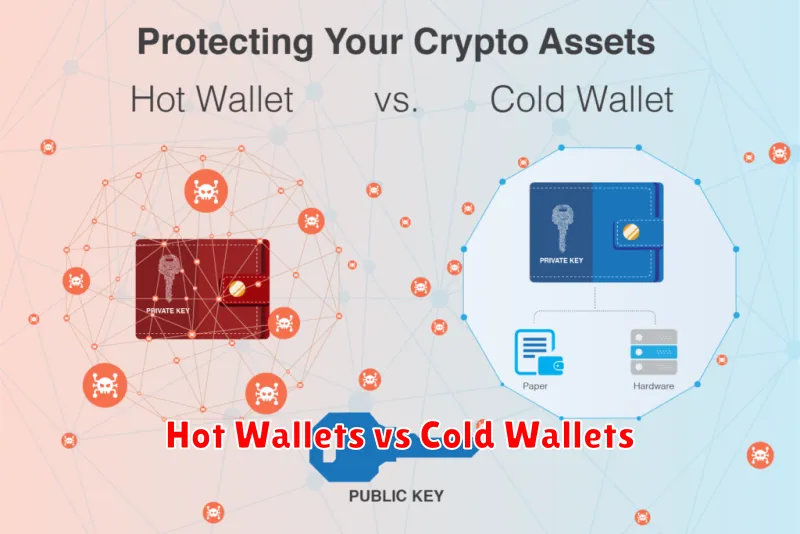
Choosing the right crypto wallet is crucial for securing your digital assets. The primary distinction lies between hot wallets and cold wallets, each offering different levels of security and convenience.
Hot wallets, connected to the internet, provide easy access to your cryptocurrency. This convenience comes at a cost: they are more vulnerable to hacking and malware. Examples include software wallets (installed on your computer or phone) and web wallets (accessed through a browser). They are ideal for frequent transactions but demand heightened security awareness.
In contrast, cold wallets, also known as hardware wallets, are offline devices specifically designed for cryptocurrency storage. This offline nature significantly reduces the risk of theft from online attacks. While offering superior security, they are less convenient for frequent trading as they require manual interaction for every transaction. They’re the preferred choice for storing large amounts of cryptocurrency for the long term.
The best choice depends on your individual needs and risk tolerance. Consider the frequency of your transactions and the amount of cryptocurrency you hold when deciding between a hot and cold wallet solution. For high-value holdings, a cold wallet is generally recommended.
Best Practices for Wallet Security

Choose a reputable wallet provider: Research thoroughly before selecting a wallet, prioritizing those with strong security reputations and positive user reviews. Consider factors like multi-signature support and established track records.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access your wallet even if your password is compromised. Use a strong and unique 2FA method.
Use strong, unique passwords: Avoid easily guessable passwords. Employ a password manager to generate and securely store complex, unique passwords for each of your wallets.
Regularly update your wallet software: Software updates often include critical security patches. Keeping your wallet software up-to-date is crucial to mitigating known vulnerabilities.
Store your seed phrase securely offline: Your seed phrase is the key to recovering your funds. Never store it digitally, and utilize a secure, physical method like a metal plate or a fireproof safe.
Be cautious of phishing scams: Be wary of suspicious emails, messages, or websites requesting your wallet details. Legitimate wallet providers will never ask for your seed phrase or private keys.
Diversify your holdings: Don’t keep all your cryptocurrencies in a single wallet. Spread your assets across multiple wallets to minimize risk in the event of a security breach.
Regularly review your transaction history: Monitor your wallet activity for any unauthorized transactions. Act quickly if you detect any suspicious activity.
Educate yourself on security best practices: Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices in the cryptocurrency space. Continuous learning is essential for protecting your assets.
Understanding Private and Public Keys
Cryptocurrency wallets utilize a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key and a public key. These keys are mathematically linked, allowing for secure transactions.
Your private key is a secret, randomly generated string of characters. It’s crucial to keep this key absolutely confidential. Think of it as your password; anyone with access to your private key has complete control over your cryptocurrency funds.
Your public key, on the other hand, is a derived value from your private key. It can be shared publicly without compromising your security. It acts like your bank account number – others can send funds to it without needing your private key.
The combination of these keys enables secure transactions. When you send cryptocurrency, your wallet uses your private key to sign the transaction, proving ownership. The recipient then uses your public key to verify the signature and receive the funds.
Protecting your private key is paramount to maintaining the security of your cryptocurrency holdings. Never share it with anyone, and use a secure wallet that employs strong encryption and security protocols.
How to Backup Your Wallet

Backing up your crypto wallet is crucial for securing your assets. The method varies slightly depending on the type of wallet (hardware, software, or paper), but the core principle remains the same: create a secure copy of your private keys or seed phrase.
For hardware wallets, note down the recovery seed phrase provided upon initial setup and store it securely, ideally offline and in multiple locations. Never store the seed phrase digitally.
For software wallets, the process often involves exporting your private keys or seed phrase. This should be done carefully, ensuring the security of the process and the storage of the backup. Again, offline and secure physical storage is paramount.
Paper wallets require printing your public and private keys or a QR code representing them. Store these in a secure, fireproof, and tamper-evident location. Consider multiple backups.
Regardless of your wallet type, treat your backup like your most valuable possession. Losing access to your backup means losing access to your cryptocurrency.
Using a Hardware Wallet for Maximum Security

A hardware wallet offers the most secure method for storing your cryptocurrency. Unlike software wallets residing on your computer or phone, a hardware wallet is a physical device that generates and stores your private keys offline. This significantly reduces the risk of hacking and malware.
These devices typically use a secure element, similar to those found in credit cards, to protect your private keys. This provides a strong defense against remote attacks. Transactions are authorized through the device’s interface, keeping your private keys inaccessible to external threats.
While hardware wallets represent a significant investment, the increased security they provide is invaluable for users holding substantial amounts of cryptocurrency or prioritizing maximum protection. They are a crucial component of a robust security strategy for safeguarding your digital assets.
Choosing a reputable brand is critical. Research different models, comparing their security features, user-friendliness, and compatibility with your preferred cryptocurrencies before making a purchase.
How to Transfer Crypto Between Wallets
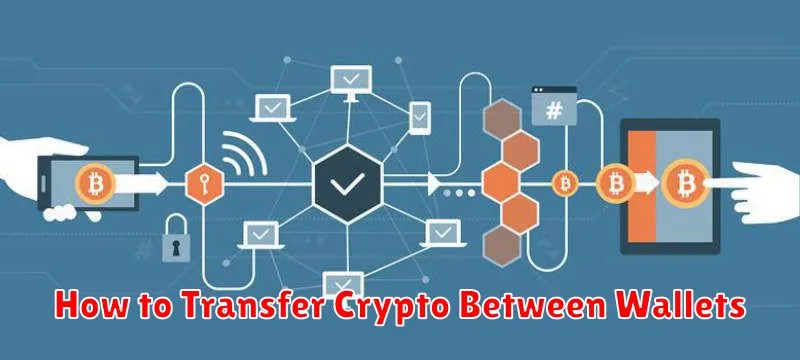
Transferring cryptocurrency between wallets involves sending your coins from one digital address to another. The process varies slightly depending on the type of wallet and cryptocurrency, but the core steps remain similar. Security is paramount; always double-check the recipient’s address before initiating a transaction.
First, you’ll need to open both your sending and receiving wallets. Within your sending wallet, locate the “Send” or “Transfer” option. You will then be prompted to enter the recipient’s wallet address. This is a unique alphanumeric string, similar to an email address, specific to each wallet. Carefully copy and paste this address to avoid errors. Next, specify the amount of cryptocurrency you wish to transfer. Most wallets will display the current transaction fee, which covers the network’s processing cost. Review all details and confirm the transfer.
After confirmation, the transaction will be broadcast to the relevant blockchain network. The processing time varies depending on the network’s congestion; some transactions are almost instant, while others may take several minutes or even hours to confirm. Once confirmed, the cryptocurrency will appear in your receiving wallet. You can usually track the transaction’s status within your wallet’s transaction history. Remember to keep your private keys and seed phrases secure at all times, as these are essential for accessing your funds.
Avoiding Common Crypto Wallet Scams

Cryptocurrency wallets, while offering convenient storage for your digital assets, are unfortunately vulnerable to various scams. Understanding these scams is crucial for protecting your investments. Phishing is a prevalent threat, where scammers impersonate legitimate platforms to trick users into revealing their private keys or seed phrases. Never share this sensitive information with anyone.
Fake websites and apps mimicking popular exchanges or wallets are another major concern. Always verify the URL and app source before interacting with any platform. Look for secure connections (HTTPS) and read reviews from trustworthy sources. Beware of unsolicited emails, messages, or calls promising high returns or free crypto, as these often lead to malicious websites or software.
Social engineering attempts often leverage emotional manipulation or pressure tactics to steal your crypto. Legitimate companies will never demand urgent action or threaten account closure. Exercise caution and verify any unexpected communications through official channels before taking any action.
Malware can compromise your device and steal your private keys. Use reputable antivirus software and keep your operating system and applications updated. Avoid downloading software from untrusted sources or clicking suspicious links.
Finally, strong password practices and enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) are vital steps in securing your wallet. Use unique, complex passwords and choose strong 2FA methods such as authenticator apps.
Why You Should Never Share Your Seed Phrase
Your seed phrase is a critical security element for your cryptocurrency wallet. It acts as the master key to access all your digital assets.
Sharing your seed phrase with anyone, even a trusted friend or family member, is incredibly risky. If someone gains access to it, they can immediately and irrevocably gain control of your entire cryptocurrency holdings. There is no recovery if this occurs.
No legitimate service or individual will ever ask for your seed phrase. Anyone requesting it is likely attempting to scam you. Remember, your seed phrase should be treated with the utmost secrecy and stored securely offline in a manner that only you know.
Protecting your seed phrase is paramount to maintaining the security of your cryptocurrency investments. Treat it like a combination to a vault, never revealing it to others.